What is Biotin?
Often hailed as the “vitamin for beauty,” biotin plays a crucial role in our health. If you’re looking for ways to improve your health, especially your hair, skin, and nails, you may have encountered B7. But what is biotin, and what makes it beneficial?
Understanding Its Function
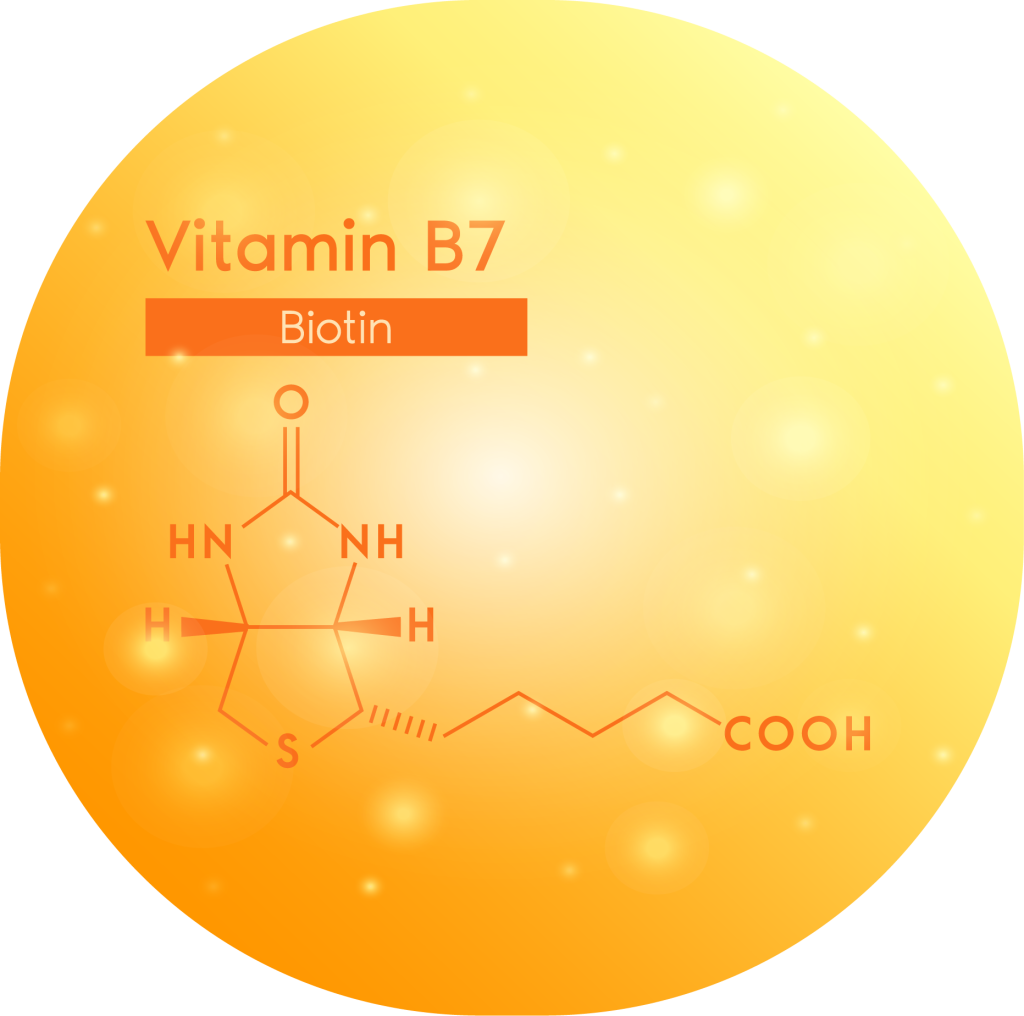
Biotin, known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H, is a water-soluble B vitamin that plays a key role in the body’s metabolism. B7 assists in converting food into energy by supporting enzymes that break down fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. The body would have a hard time converting nutrients into the energy it needs without it.
What is D-Biotin?
D-biotin is the naturally occurring, biologically active form of biotin. It’s the version most commonly found in supplements and is responsible for the vitamin’s various health benefits.
Biotin vs. Collagen: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to hair and skin health, biotin and Collagen often come up. While they share some benefits, they’re pretty different:
- As mentioned, biotin is a B vitamin that supports keratin production, benefiting hair, skin, and nails. It’s primarily consumed through diet and supplements.
- Collagen: Collagen is a protein that provides structure to the skin, bones, and connective tissues. It’s essential for maintaining skin elasticity and strength.
What is Better for Thinning Hair: B7 or Collagen?
The decision between biotin and Collagen depends on the reason for thinning hair. B7 is helpful if the problem stems from a deficiency, as it promotes keratin production. On the other hand, Collagen can enhance hair strength and elasticity, making it a good option for those with weak or brittle hair. Consulting a healthcare provider can help you identify the best choice for your needs.
What is Biotin Shampoo Good For?
Biotin shampoos are well-known for enhancing hair health. They often include additional ingredients that promote scalp health and strengthen hair. While they can be beneficial, it is crucial to maintain a balanced diet with sufficient B7 intake for optimal results.
Transforming your nutrition
Transforming your nutrition starts with smart meal planning. Discover quick and delicious recipes on our Fuel Board that the whole family will love. To streamline your grocery shopping and meal prep, don’t miss out on the FeedMeFood meal planner and Pantry Inventory App —your key to healthier, hassle-free meals!