VITAMIN B12- COBALAMIN
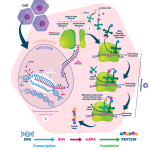
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in maintaining a healthy body. This nutrient is vital for numerous body functions, making it necessary to maintain optimum levels. Vitamin B12 is water soluble, which means it cannot be stored by the body, making it even more crucial to ensure that we get enough of it through our diet. Foods rich in vitamin B12 include meat, fish, dairy products, eggs, and fortified cereals.
Cobalamin is a nutrient that plays an integral role in our body’s functioning. Ensuring that we get enough of this vital nutrient is critical for maintaining good health. People who are at a higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency include vegans and vegetarians, older adults, and those who have had gastrointestinal surgery. If you are concerned about your vitamin B12 levels, consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian who can help you ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs.